
Do you have an increased chance of catching COVID-19?
And if you do catch it, what are the odds of severe symptoms and hospitalization?
Your genes may hold the answer, new research is discovering. A recent genome-wide association study (GWAS) has revealed that certain groups are more likely to have severe COVID-19 symptoms than others.
The ABO Blood Group, which determines your blood type, was found to be associated with increased risk for severe COVID symptoms. People with Blood Type A had a higher risk for respiratory failure, nearly 50% higher than other blood groups. Meanwhile, people with blood type O were found to be two thirds as likely to experience respiratory failure as other blood groups.[1]
The study also made mention of the genes encoding the ACE2 receptor. This enzyme receptor is a known entry point for the virus, so certain genes there are also associated with increased susceptibility to the virus, including an increased chance of being put on a ventilator.
While these data points are somewhat disturbing, they can be potentially useful. Based on these GWAS results, CRI Genetics has developed a report that determines whether or not your genes indicated you have a higher risk for COVID-19 severity.

A sample COVID-19 Severity Report.
So far, 13.23% of our customers have received a “Higher Risk” report, meaning they could be at higher risk for experiencing more severe COVID symptoms. That’s more than 1 in 8 people who have taken the test.
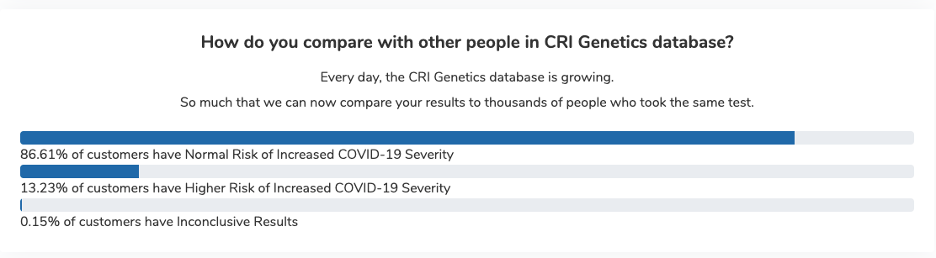
So far, 1 in 8 of our customers has a higher risk for COVID-19 Severity.
Of course, these genetic factors are only one piece of the puzzle—your distancing from others, personal hygiene habits, and wearing of PPE could all affect your chances to a far greater degree. And everyone should take precautions. To learn more about the COVID-19 Severity Test from CRI, click here.
https://www.the-scientist.com/news-opinion/two-genetic-regions-linked-with-severe-covid-19-67619; https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.05.31.20114991v1.full.pdf+html.